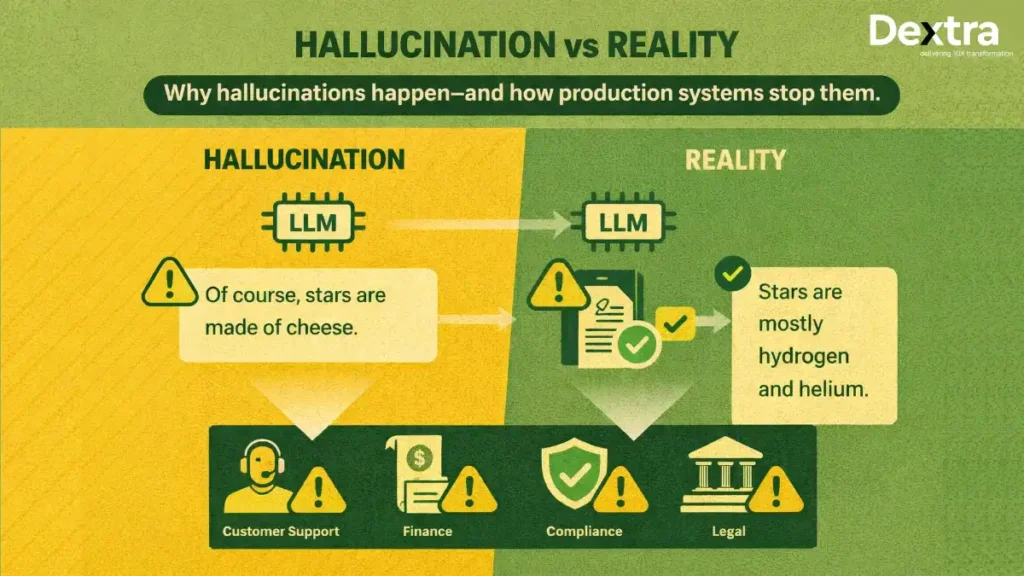
Large language models or LLMs are transforming the way companies develop intelligent applications. They can help with customer assistants, internal business applications, and research tools. However, one challenge stands tall: LLM hallucinations. These are cases where the model produces information that seems confident but is factually incorrect or misleading.
These issues are not just theoretical. Gartner research shows that large language models exhibit frequent inaccuracies, often referred to ashallucinations. It can undermine user trust and performance if not properly managed.
At the same time, adoption of LLM-based generative AI is booming. Gartner predicts that more than 80% of enterprises will have used GenAI APIs or deployed GenAI-enabled applications by 2026, meaning the challenge of managing hallucinations will affect a large portion of production systems.
For teams putting AI into real systems, hallucinations are more than just an academic issue. They can harm trust, damage brand reputation, and create real business risk. This article presents a production-ready guide on how to reduce LLM hallucinations in real systems—technology stacks where reliability matters. It is designed to help technical and non-technical readers understand the full picture, from why hallucinations happen to practical safeguards that work in live environments.
Why Hallucinations Matter in Production AI Systems?
Modern production AI systems are expected to deliver accurate, trustworthy results. In research settings, occasional errors might be acceptable. In real products, they are not.
Imagine:
- A customer support bot is giving incorrect technical guidance.
- An internal report generator fabricating financial data.
- A compliance tool inventing legal interpretations.
In each case, the impact is not just an error—it’s a failure in the user experience and a potential business liability.
Hallucinations happen because of how LLMs work. They predict the next most likely words based on patterns in data, not based on real understanding. While this enables flexible language generation, it also makes the model prone to confidently creating plausible but false content.
Solving this requires more than prompts or model tweaks. It needs a system-level approach built into the architecture.

Understanding Where Hallucinations Enter the LLM Pipeline
To reduce hallucination risk in production, it helps to look at where they occur in the system.
Pre-Generation Risks
Before the model generates a response, the input must be clear and complete. If the prompt is vague or missing essential context, the model fills in gaps with guesses. Even the best models can hallucinate when they lack precise instructions or reliable grounding data.
Generation-Time Risks
During output generation, the model relies on probabilities. This is where confident but incorrect answers can emerge, especially when:
- The model isn’t grounded in verified information.
- There’s a long context with mixed relevance.
- The task requires real facts instead of creative language.
Post-Generation Risks
Even a well-formed prompt and accurate model can output inaccurate results if there’s no verification layer. Without checking results against trusted data, systems often pass hallucinated text directly to users.
Why RAG Alone is Not Enough
Many teams use RAG systems (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) to reduce hallucinations. RAG works by pulling data from a knowledge store and using it to guide the model’s output. While this is valuable, it is not a cure-all.
Typical RAG Failure Modes
- Irrelevant Retrieval: The system fetches data that doesn’t truly relate to the question.
- Stale Embeddings: Outdated representations cause mismatches between query and data.
- Similarity ≠ Truth: A high similarity score doesn’t guarantee correctness.
When retrieval fails, the model still generates text. It may weave retrieved snippets into confident but misleading answers.
To truly mitigate hallucinations, RAG must be paired with verification and architectural safeguards.
Designing a Validation Layer for LLM Outputs
A validation layer checks outputs before they reach users. This is one of the most effective safeguards against hallucinations in production systems.
Output Validation Techniques
- Schema and Format Validation
For structured replies (e.g., dates, lists, numeric answers), check whether the result fits the expected format. - Claim Verification
Match statements against reliable sources. For example, if the model claims “X happens in year Y,” verify this with trusted databases. - Confidence Thresholds
Many models provide confidence or probability signals. Using thresholds can help filter low-confidence or risky outputs.
Self-Consistency and Cross-Checking
Ask the model the same question multiple ways and compare answers. If results differ significantly, the system can flag uncertainty and fall back to safer responses.
Refusal Strategies
Teach the system to say “I don’t know” or steer away from answers it cannot verify. A refusal is better than a fabricated response.
With a validation layer, the system becomes more like a responsible partner rather than an unconstrained language generator.
Tool Grounding: Reducing Free-Text Hallucinations
One of the most powerful ways to reduce hallucinations is tool grounding. Instead of allowing the model to generate unconstrained text, certain tasks should be handled via deterministic tool calls.
Why Tools Help
Tools are programmed to do specific jobs:
- Query a database
- Compute a result
- Validate a condition
When a model calls a tool, it gets structured, reliable data back, which limits hallucination.
Designing Tool-First AI Agents
A production AI agent can follow this decision logic:
- Is this question best handled by a tool?
- If yes, call the tool.
- If no, proceed with generation.
- Validate tool results before returning.
- Fallback paths for ambiguous or unsupported tasks.
For example, a weather tool can return exact forecasts. The model shouldn’t guess weather details because it doesn’t have access to real-time data.
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL): Designed, Not Bolted On
Human review is often cited as a halo solution for hallucinations. But without clear process rules, it becomes slow and expensive.
In production systems, HITL should be intentional and selective.
When HITL Is Necessary
Use human review when:
- The model output could cause legal or safety issues.
- Reliable automated validation is not possible.
- Confidence scores are below a safe margin.
Cost-Aware HITL Design
Humans should not review every response. Instead:
- Only low-confidence or high-risk outputs go to human checkers.
- Feedback from humans trains the system to improve.
This creates a feedback loop that strengthens the model and reduces hallucinations over time.
Balancing Accuracy, Latency, and Cost
Every system design involves trade-offs. In real AI systems, it’s important to balance:
- Accuracy: How correct are outputs?
- Latency: How fast does the system respond?
- Cost: How much compute and human effort does it use?
Accuracy vs Latency
More verification steps may improve quality, but slow down responses. For interactive systems, this requires smart scheduling:
- Fast, lightweight checks for common questions
- Deeper checks for risky queries
Cost Control Strategies
- Use smaller models for low-risk tasks, and larger models only where needed.
- Cache verified answers to avoid repeated computation.
- Tier validation steps to escalate only when necessary.
By consciously optimizing these factors, teams can build systems that are both trustworthy and efficient.
Measuring and Monitoring Hallucinations in Production
To reduce hallucinations, it’s essential to measure them.
Key Metrics to Track
- Hallucination Rate: Percentage of outputs that fail validation.
- Refusal Rate: How often the system says “I don’t know.”
- Correction Signals: When users correct or reject responses.
These metrics help teams understand where the system succeeds and where it needs improvement.
Continuous Improvement Loop
Hallucination monitoring should feed back into:
- Model tuning
- Retrieval and embedding updates
- Prompt and tool logic adjustments
With consistent tracking and iteration, systems steadily improve.
A Production-Ready Hallucination Mitigation Architecture
Here is a layered defense strategy for real systems:
- Input Validation: Check prompt completeness and clarity.
- RAG with Safeguards: Ground retrieval with relevance and freshness checks.
- Tool Grounding: Use deterministic tools for factual tasks.
- Output Validation: Schema checks, confidence thresholds, and claim verification.
- HITL Escalation: Selective human review for edge cases.
- Monitoring & Metrics: Track hallucination KPIs and refine systems.
This architecture turns hallucination handling from ad-hoc reactions into a responsible and measurable system feature.
When to Seek Expert Help?
Some systems are simple. Others are complex and risky. In many enterprise cases, teams benefit from expert support.
Signs that expert help is needed:
- Hallucinations are frequent or damaging.
- The system affects regulatory compliance.
- Live users interact with your model at scale.
- Internal teams lack experience with LLM architecture.
Dextralabs offers AI system design audits, architecture planning, and deployment services. Teams can engage experts to:
- Review existing system design
- Identify failure points
- Implement reliable mitigation strategies
- Deploy with monitoring and governance
Conclusion
Reducing hallucinations in production AI systems is not a one-time task. It is a system engineering challenge. To develop systems in which users will trust them, there must be an understanding of where these hallucinations are happening and how these safeguards can be layered in as validation layers, tool grounding, and HITL.
A careful mix of accuracy, latency, and cost, coupled with constant monitoring and optimization, can transform the promising experiment that is generative AI into a trustworthy business resource.
Ready to Build Trustworthy, Production-Grade AI?
If hallucinations are holding your AI systems back, Dextralabs can help. Reach out today for a tailored audit or production readiness review. Let expert engineers design reliable, scalable AI systems that match your business needs.
FAQs:
Q. How can LLM hallucinations be minimized in real-world systems?
LLM hallucinations can only be minimized, not eliminated, by designing AI systems with control at every layer. This means grounding model outputs in verified data, enforcing structured retrieval through well-designed RAG pipelines, validating outputs before execution, and limiting autonomous actions. Enterprises that treat hallucinations as an architectural risk rather than a model flaw achieve significantly more reliable outcomes.
Q. How do you reduce hallucinations when an LLM gives factual or advisory responses?
For factual advice, hallucination risk is reduced by preventing the model from “guessing.” This requires strict data grounding, source-aware retrieval, and explicit refusal behavior when evidence is missing. High-risk advisory systems should also implement confidence scoring and human-in-the-loop review so uncertain outputs are never blindly trusted.
Q. Can Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) reduce LLM hallucinations?
Yes, but only when implemented correctly. RAG reduces hallucinations by forcing the model to respond using retrieved, relevant documents rather than latent memory. However, poorly designed RAG systems can increase hallucinations if retrieval returns irrelevant, outdated, or conflicting information. RAG must include relevance filtering, source validation, and context limits to be effective.
Q. Why do RAG systems still hallucinate in production?
RAG systems hallucinate when retrieval quality is weak, context windows are overloaded, or the model is not constrained to retrieved sources. Common failure modes include embedding drift, stale vector databases, over-broad similarity search, and missing document provenance. Without monitoring and evaluation, these failures remain invisible until business impact occurs.
Q. What architectural patterns reduce hallucinations beyond prompt engineering?
Prompt engineering improves surface-level responses but does not address systemic risk. Production-grade mitigation requires architectural patterns such as tool grounding, rule-based execution layers, output validators, confidence thresholds, and fallback logic. These patterns ensure that hallucinations are intercepted before they propagate into downstream systems.
Q. How does tool grounding help prevent hallucinations?
Tool grounding restricts the model from inventing answers by requiring it to call deterministic tools—such as databases, APIs, or calculators—for factual queries. Instead of generating free-text responses, the LLM becomes a reasoning layer that orchestrates verified tools, significantly reducing hallucination risk in enterprise workflows.
Q. What role does human-in-the-loop (HITL) play in hallucination control?
Human-in-the-loop systems are essential for high-impact use cases such as finance, legal, healthcare, and enterprise decision automation. HITL acts as a risk valve—low-confidence outputs are routed for review, corrections are logged, and feedback is fed back into the system. This approach balances automation with accountability.
Q. What is the most common mistake enterprises make when addressing hallucinations?
The most common mistake is assuming hallucinations are a temporary model issue that will disappear with better prompts or newer LLMs. In reality, hallucinations are inherent to probabilistic systems. Enterprises that succeed design control-first AI architectures that assume errors will happen and focus on preventing those errors from causing harm.
Q. What does a production-grade hallucination mitigation playbook include?
A production-ready playbook includes grounded data pipelines, robust RAG architecture, output validation layers, tool-based execution, human-in-the-loop workflows, observability dashboards, and governance controls. Together, these components transform LLMs from experimental tools into reliable enterprise systems.