How LLMs Transform Data Quality from Rule-Based Compliance to Intelligent Reasoning? According to Gartner research, poor data quality costs organizations an average of $12.9 million annually and Harvard Business Review finds that only 3% of companies’ data meets basic quality standards. Traditional data validation approaches, regex patterns, hard-coded rules, and static SQL checks, struggle with the messiness and complexity of modern enterprise data.
Enter prompt engineering, the discipline of crafting intelligent queries that enable LLMs to reason about data quality like expert auditors. Rather than enforcing rigid syntactic constraints, LLM-powered validation assesses whether data makes logical sense in context, catching subtle inconsistencies, semantic errors, and impossible combinations that traditional rules miss.
At Dextra Labs, we’ve pioneered LLM-driven data quality frameworks across UAE, USA, and Singapore deployments, achieving:
- 87% reduction in false positives compared to rule-based systems
- 60% faster anomaly detection in unstructured data
- $2.4M average annual savings from preventing downstream errors
- 45% improvement in data audit coverage
This comprehensive guide reveals how prompt engineering transforms data validation, the techniques that deliver production-grade results, and how Dextra Labs architects intelligent data quality systems for enterprises.
Also Read: From Task-Based AI Agents to Human-Level Research Systems: The Missing Layer in Agentic AI
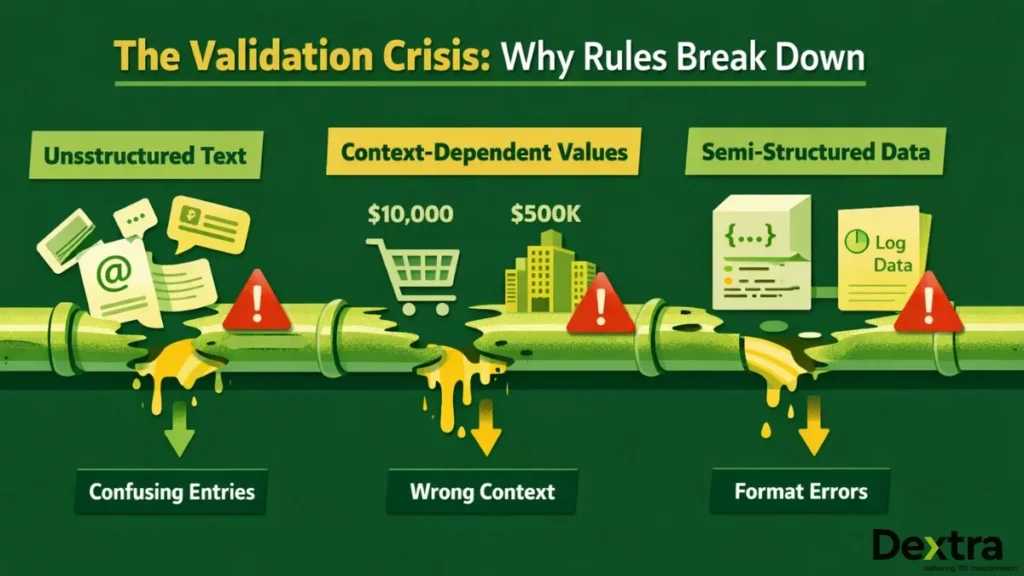
The Validation Crisis: When Rules Break Down
For years, data validation meant strict conditions—hard-coded rules that flagged when a number fell out of range or a string didn’t match expectations. These worked fine for structured, predictable systems. But modern organizations don’t operate in predictable systems anymore.
Consider the challenges:
Unstructured Data Explosion: Only 3% of companies’ data meets basic quality standards (Harvard Business Review). When dealing with customer feedback, email correspondence, or scraped web content, traditional validators can’t distinguish between legitimate variation and actual errors.
Context-Dependent Validity: A transaction of $10,000 might look suspicious in a grocery dataset but trivial in B2B sales. The same “outlier” in one domain is standard in another. Static rules can’t encode this contextual intelligence.
Semi-Structured Complexity: Modern datasets mix structured fields with free-text entries, JSON objects with CSV exports, timestamps with natural language descriptions. Validation logic that worked for clean relational databases becomes unwieldy when applied to real-world data pipelines.
The result? Organizations spend massive resources building and maintaining brittle validation systems that still let bad data through. Employees can waste up to 27% of their time dealing with data issues (Actian), and it costs ten times as much to complete a unit of work when data is flawed compared to when they are perfect (Harvard Business Review).
Also Read: Mastering LLM Outputs: A Human Guide to Tuning the 7 Key Parameters
Enter Prompt Engineering: Validation as Reasoning
Prompt engineering changes the game by treating validation as a reasoning problem rather than a syntactic one. Instead of asking “does this field match regex X? “we can ask LLMs: “does this record make logical sense given the context of the dataset?”
This is a shift from enforcing constraints to evaluating coherence. And the implications are significant for enterprises dealing with complex, evolving data landscapes.
How LLM-Driven Validation Works?
LLM-driven validation is powerful because it is able to internalize context, spot patterns, and provide rationale. Here are the things that separate it from the rest:
Semantic Understanding: LLMs not only match patterns but also grasp the meaning of data. They are able to tell that “NYC” and “New York City” are two different ways of saying the same thing, “Director of Engineering” and “Engineering Director” are the same in function, and the birth date of “2025” for a company executive is not a likely event.
Domain Intelligence: Proper prompt engineering can make the model understand the specific area. Get the model to know that healthcare claim amounts range from $50 to $50,000 and above for B2B datasets, customer email addresses should have corporate domains, or that retail operations’ transaction timestamps should match business hours.
Explainable Validation: When an LLM cannot stand one value and its entry as suspicious, you are free to ask the LLM to justify its decision. The use of phrases like “explain briefly why you think this value may be incorrect” fosters a self-check loop, making the process of the model more reliable and transparent.
Adaptive Logic: Prompt-based validation is unlike static rules and can adapt to new patterns. Data transformations occur, and the prompts may be redefined quicker and easier than changing validation code.
Also Read: 7 Prompt Engineering Templates That Actually Work
Practical Implementation: From Theory to Production
The Architecture of Intelligent Validation
Pre-Processing Layer: Before records hit your production database, an LLM reviews them for anomalies—wrong formats, improbable combinations, missing context. The model doesn’t just validate syntax; it evaluates plausibility.
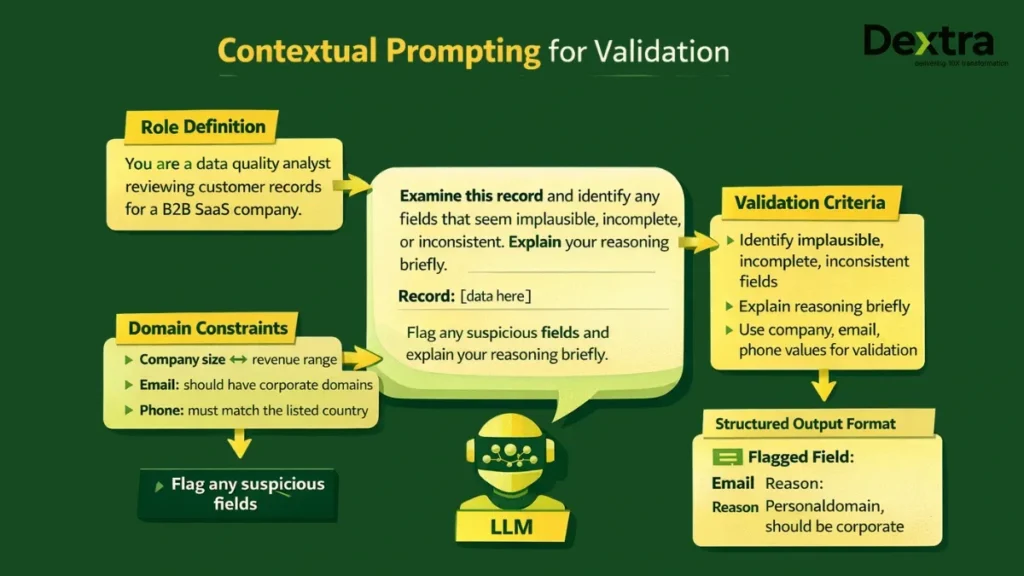
Contextual Prompting: Effective prompt engineering for data validation must encode domain context. A basic validation prompt might look like:
You are a data quality analyst reviewing customer records for a B2B SaaS company.
Examine this record and identify any fields that seem implausible, incomplete, or inconsistent:
– Company size should align with revenue range
– Email domains should be corporate, not personal
– Phone numbers should match the listed country
– Job titles should be reasonable for the company size
Record: [data here]
Flag any suspicious fields and explain your reasoning briefly.
Iterative Refinement: The same dataset can yield dramatically different validation quality depending on how questions are phrased. Teams need to iterate on wording—adding explicit reasoning cues, setting confidence thresholds, or constraining output format. This experimentation turns prompt engineering from a one-time task into an ongoing optimization process.
Human-in-the-Loop: LLM validation works best when combined with human review. The model highlights entries that “look suspicious,” analysts review and confirm, and those cases feed back as training data for refined prompts. This creates a virtuous cycle where validation improves over time.
Real-World Applications
ETL Pipeline Integration: Data teams are plugging prompt-based checks directly into extract, transform, load pipelines. Models like GPT-4 or Claude act as intelligent gatekeepers, reviewing records before they enter production systems.
Customer Data Cleansing: For CRM and marketing platforms, LLM validation can identify duplicate records, normalize formatting inconsistencies, and flag outdated information—all with contextual understanding that rigid rules lack.
Financial Transaction Monitoring: In fintech applications, prompt-based validation helps detect anomalous transactions, verify account information, and ensure regulatory compliance with explainability that traditional systems can’t provide.
Log Analysis and Error Detection: For DevOps and system monitoring, LLMs can parse unstructured log files, identify error patterns, and flag anomalies that would be missed by keyword-based alerting.
Also Read:- Prompt Engineering for ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini
The Business Case: Why This Matters Now?
The financial stakes make prompt engineering for data quality a strategic imperative, not just a technical curiosity:
Cost Reduction: With organizations losing $12.9-15 million annually to poor data quality (Gartner), even modest improvements in data validation deliver substantial ROI.
Productivity Recovery: If employees spend up to 50% of their time managing bad data (Harvard Business Review), automated LLM validation can reclaim hundreds of hours annually for strategic work instead of manual data cleanup.
AI Readiness: As organizations invest in AI and machine learning, data quality becomes the bottleneck. Clean, validated data is the foundation for successful AI initiatives.
Regulatory Compliance: In banking, insurance, and healthcare, regulators demand audit-ready systems where every decision is traceable to source data. Prompt-based validation provides explainability that static rules can’t match, making compliance audits smoother and more defensible.
Also Read: Top 7 Enterprise Use Cases of Prompt Engineering in AI-Powered Workflows
Challenges and Considerations
While prompt engineering for data validation offers compelling benefits, organizations need to address several practical challenges:
Cost and Scalability
LLMs can be expensive to query at large scale. For high-volume pipelines processing millions of records daily, teams need to balance validation quality against API costs. Strategies include:
- Selective validation: Use LLM checks for high-value or high-risk records while applying traditional rules to routine data
- Batch processing: Group records for validation to reduce API overhead
- Caching: Store validation results for similar records to avoid redundant queries
- Hybrid approaches: Combine rule-based filters with LLM validation for suspicious cases only
Model Reliability and Drift
LLMs can make mistakes or miss subtle issues. Organizations need robust monitoring:
- Validation loops: Implement checks where the LLM justifies its reasoning, catching spurious flags
- Confidence thresholds: Only act on high-confidence validations; route ambiguous cases to human review
- Continuous evaluation: Track validation accuracy over time and refine prompts as data patterns evolve
Domain Knowledge Encoding
The quality of prompt-based validation depends entirely on how well you encode domain intelligence. Generic prompts produce generic results. Effective implementation requires:
- Collaboration between data engineers and domain experts to capture business rules
- Documentation of valid ranges, expected patterns, and contextual constraints
- Regular prompt updates as business requirements change
The Dextralabs Approach: Production-Ready Data Validation
At Dextralabs, our LLM consulting and prompt engineering services help enterprises and SMEs build data validation systems that actually work in production. Our approach combines technical expertise with practical implementation:
Assessment and Strategy: We start by understanding your data landscape—what validation challenges you face, where data quality problems cause the most pain, and what success looks like for your organization.
Prompt Architecture Design: We build validation prompts that encode your domain knowledge, business rules, and contextual constraints. This isn’t generic prompt engineering—it’s custom logic designed for your specific data challenges.
Pipeline Integration: We help you integrate LLM validation into existing data pipelines, whether that’s ETL processes, real-time data streams, or batch processing systems. The goal is validation that happens automatically, not as an afterthought.
Monitoring and Optimization: We implement tracking systems that measure validation accuracy, flag edge cases, and identify opportunities for improvement. Prompt engineering for data quality is an ongoing discipline, not a one-time project.
Cost Optimization: We help you balance validation quality against operational costs through hybrid architectures, intelligent caching, and selective validation strategies.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Data Quality
As we move further into 2025, data quality is becoming less about manual cleanup and more about intelligent automation. Several trends are accelerating this shift:
Agentic AI for Data Quality: Agentic AI systems will validate, trace, and fix data before it breaks business systems, moving from flagging problems to automatically correcting them.
Self-Healing Pipelines: Instead of flagging problems for human review, next-generation systems will use LLMs to automatically correct data issues based on learned patterns and domain knowledge.
Real-Time Validation: As processing speeds increase and costs decrease, prompt-based validation will move from batch processing to real-time checks, catching data problems at the point of entry rather than downstream.
Cross-Domain Intelligence: LLMs trained on diverse datasets will bring validation insights from one industry to another, recognizing patterns and anomalies that domain-specific tools would miss.
The Path Forward: From Rules to Reasoning
The shift from rule-based data validation to prompt-engineered reasoning represents a fundamental change in how we think about data quality. Static rules asked “does this match a pattern?” Prompt engineering asks “does this make sense?”
This isn’t just a technical distinction—it’s a strategic one. Organizations that master prompt-based data validation will spend less time fixing data problems and more time using clean data to drive decisions. They’ll catch issues earlier, understand root causes better, and adapt faster as their data landscape evolves.
The best data engineers aren’t just SQL experts anymore—they’re prompt architects who know how to encode domain intelligence in ways that are interpretable and adaptable. The frontier of data quality isn’t defined by stricter rules, but by asking better questions.
Conclusion: Building Trust Through Intelligent Validation
Data validation has always been about trust—trusting that what you’re analyzing reflects reality. LLMs, through prompt engineering, bring that trust into the age of reasoning. They don’t just check if data looks right; they assess if it makes sense.
With organizations losing $3.1 trillion annually to poor data quality (IBM), the case for better validation is clear. Prompt engineering offers a path forward: validation that’s more intelligent, more adaptable, and more aligned with how businesses actually use data.
At Dextralabs, we help enterprises and SMEs make this transition. Whether you’re in the UAE, USA, or Singapore, our team brings hands-on experience in building LLM-powered data validation systems that work in production. We know how to balance accuracy with cost, encode domain knowledge effectively, and integrate prompt-based validation into existing data infrastructure.The shift is happening. The question isn’t whether prompt engineering will transform data quality—it’s whether your organization will lead that transformation or follow it.
FAQs:
Q. What is prompt engineering for data quality?
Prompt engineering for data quality is the practice of designing structured prompts that enable LLMs to validate, reason about, and explain data issues beyond traditional rule-based checks. It focuses on contextual correctness, semantic consistency, and logical plausibility rather than simple pattern matching.
Q. How do LLMs improve data validation compared to rule-based systems?
LLMs improve data validation by reasoning over context, domain knowledge, and relationships between fields. Unlike rule-based systems that rely on static thresholds or regex patterns, LLMs can detect semantic errors, improbable combinations, and contextual anomalies that rigid rules typically miss.
Q. Can LLMs validate unstructured and semi-structured data?
Yes. LLMs are particularly effective at validating unstructured and semi-structured data such as text fields, logs, emails, JSON objects, and mixed-format datasets. They can interpret meaning, normalize variations, and identify inconsistencies that traditional SQL or schema validators cannot process reliably.
Q. Is LLM-based data validation explainable and auditable?
LLM-based validation can be made explainable by prompting the model to justify why a value is flagged as suspicious. These explanations create an audit trail that supports regulatory compliance, internal reviews, and trust in automated validation decisions.
Q. How is prompt-based data validation used in production systems?
In production, prompt-based validation is integrated into ETL pipelines, real-time ingestion layers, and data quality gates. LLMs act as intelligent reviewers—flagging high-risk records, validating contextual integrity, and routing uncertain cases to human reviewers when required.
Q. Does LLM data validation replace traditional rules completely?
No. The most effective architectures use a hybrid approach. Rule-based checks handle deterministic validations at scale, while LLMs are applied selectively for high-impact, ambiguous, or context-sensitive records. This balance ensures accuracy, performance, and cost control.
Q. What are the main challenges of using LLMs for data quality?
Key challenges include managing inference costs, ensuring consistent outputs, handling model drift, and correctly encoding domain knowledge into prompts. These are addressed through selective validation, confidence thresholds, monitoring loops, and continuous prompt refinement.
Q. Is prompt engineering for data quality suitable for regulated industries?
Yes. In industries such as banking, insurance, and healthcare, prompt-engineered validation supports regulatory compliance by providing explainable decisions, traceable logic, and context-aware anomaly detection—capabilities that static rules often lack.