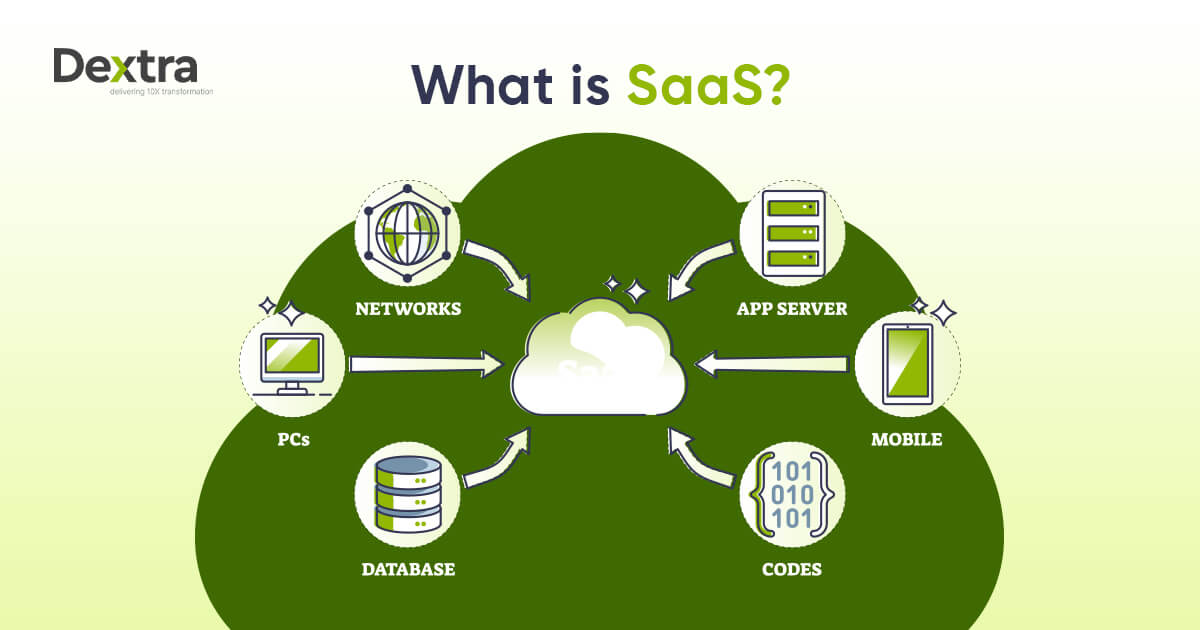
SaaS is a method for creating and delivering software for a service-based business. Rather than purchasing and installing software on your computer, you can access it online via a web browser.
This model lets you use the software without worrying about updates or storage because the provider manages everything. SaaS is popular because it is simple to use and available anywhere with an internet connection.
Let’s get into the details of what is software as a service and what is SaaS business.
What Does SaaS Stand For?
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud-based model in which software is supplied over the Internet. This lets users access the software via a web browser rather than installing or maintaining it on their local devices.
Unlike traditional software which needs a one-time purchase and installation, SaaS is based on a subscription model. Customers receive the most recent upgrades and features automatically.
The global SaaS market is expanding rapidly, with a compound annual growth rate of 27.5%. This development is due to AI-boosted sectors such as retail and manufacturing.
The History of SaaS
Now that you know what is SaaS software, let’s get into its history. Software as a Service originated in the 1960s with the goal of time-sharing, which allowed several users to access a central mainframe computer via terminals.
However, it wasn’t until the 1990s that the framework for SaaS as we know it was created. With the rise of the internet, organizations such as Salesforce began delivering software applications via web browsers.
This strategy transformed software delivery by reducing the requirement for organizations to install and maintain software on individual devices. Owing to its low cost and scalability, SaaS grew rapidly in the early 2000s.
As cloud computing technology advanced, SaaS became the primary software distribution mechanism. Today, SaaS has many applications, such as customer relationship management (CRM) and communication and collaboration tools.
What Are the Benefits of SaaS?
SaaS providers handle all aspects of the program such as security and server maintenance. But what about the benefits of this model?
Using SaaS can benefit you in a lot of ways and some benefits are listed below:
1) Cost Savings
SaaS eliminates the need for large upfront investments in software licenses and hardware. A subscription-based model allows firms to pay only for what they use, making budgeting easier. It also eliminates the need for in-house IT support and brings down operational costs.
2) Scalability
SaaS solutions are adaptable to changing business needs. Whether you’re adding new users or growing your services, SaaS lets you easily alter your subscription. This flexibility allows you to build your business without being limited by your software capabilities.
3) Accessibility and Flexibility
SaaS programs offer accessibility and flexibility, which allows users to operate from any device with an internet connection. In a SaaS model, you can work remotely, stay productive, and be updated with your mobile phone.
4) Provider-Managed Updates and Maintenance
SaaS gives the benefit of automatic updates and maintenance. You immediately get the most recent features and security patches without having to install them manually. This makes sure that the program is always up to date, lowering the chance of flaws.
5) Easy Integration
SaaS systems give easy integration with other software and services. This makes it easier for companies to create a united tech environment by linking different technologies for greater efficiency. Furthermore, many SaaS solutions give APIs that help with custom integrations.
6) Rapid Deployment
SaaS allows companies to get up and running without long installation processes quickly. You can access the product practically immediately after subscribing which reduces the time to value. This speedy deployment is especially useful for firms that need to implement solutions quickly to stay competitive.
7) Better Security
SaaS providers give better security and stronger levels of protection than other organizations. To protect user data, they deploy advanced encryption and follow industry standards. This ensures that your data is securely stored and that strong safeguards are in place to prevent breaches.
8) Reduced IT Pressure
Outsourcing software administration to a SaaS provider relieves the pressure on in-house IT workers. This helps IT professionals concentrate on more strategic duties than ordinary maintenance and troubleshooting. As a result, the total efficiency and production of the IT department can be greatly increased.
What Is SaaS Company? 8 Great Examples of SaaS!
A SaaS company gives software programs on a subscription basis via the Internet. This lets users access and use the software without installing or maintaining it locally. Here are some examples of SaaS:
1) Salesforce
Salesforce is a leading SaaS CRM platform. It helps companies handle sales, marketing, and customer service from a unified platform. Salesforce helps businesses manage client contacts and provide thorough data, increasing productivity and customer happiness.
2) Microsoft 365
Microsoft 365 provides cloud-based versions of popular productivity products such as Word and PowerPoint. You can use these products from any device that has an internet connection. This allows you to collaborate and work remotely. Microsoft 365 also features OneDrive online storage which helps users to securely store and share files.
3) Slack
Slack is a SaaS tool that helps teams communicate and collaborate. It provides channels for organized chats and simple connections with tools and services. Slack boosts team productivity by centralizing communication and enabling real-time collaboration, even among distant or distributed teams.
4) Google Workspace
Google Workspace offers cloud-based productivity tools such as Google Docs and Google Meet. These technologies let users create and collaborate on documents and presentations in real time. Google Workspace is popular among educational institutions and organizations due to its simplicity and easy integration.
5) Dropbox
Dropbox is a SaaS platform for cloud storage and file sharing. It allows users to save files online and view them from any device, guaranteeing that data is always available. Dropbox also promotes cooperation by allowing users to share files and folders with others, making it easier for them to work together on projects.
6) Zoom
This SaaS tool allows video conferencing and online meetings. It gained popularity during the COVID-19 epidemic when businesses and schools switched to remote employment and online learning. Zoom is a popular virtual communication option because it provides high-quality video and audio, as well as screen sharing and recording capabilities.
7) Shopify
Shopify is a SaaS e-commerce platform that helps businesses develop and manage online stores. It provides many customized templates and inventory management capabilities. That makes selling things online easier for businesses of all sizes, from startups to major corporations.
8) Adobe Creative Cloud
Adobe Creative Cloud is a creative software suite that is available as a SaaS option. It includes popular programs such as Photoshop and Premiere Pro, which are required for graphic design and digital content creation. Adobe Creative Online offers regular upgrades and collaboration tools that assist creative professionals.
SaaS Vs. PaaS Vs. IaaS
Here is the difference between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS:
1) SaaS
SaaS helps customers to access software programs through the Internet. These programs are hosted and managed by a third-party source, so users do not need to install or update the software on their own devices. SaaS is appropriate for end-users who require ready-to-use software for tasks such as email or CRM. Examples of SaaS are Google Workspace and Dropbox.
2) PaaS
PaaS is a cloud-based platform that allows developers to build and deploy applications without worrying about infrastructure. It provides a foundation of pre-built tools and services, such as databases and development environments, allowing developers to concentrate on code and application logic. PaaS is useful for developers who need a simplified environment to build and deploy apps swiftly. Examples of PaaS are Microsoft Azure and Heroku.
3) IaaS
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the Internet, including servers and networking. Users can rent and manage these resources to construct and execute their applications, giving them complete control over the infrastructure.
IaaS is appropriate for IT managers and developers who need scalable and adaptable resources for hosting websites or managing massive datasets. Some examples of IaaS are Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud Platform.
What Is SaaS Pricing?
Here are some pricing models of SaaS:
1) Subscription Based Pricing
Subscription-based pricing is the most popular model for SaaS, with users paying a monthly or annual price to use the software. This charge often has the cost of software usage and support. Subscription plans come in tiers with varying features and user access.
2) Per-User Pricing
Customers are charged based on the number of users or seats accessing the software. This technique is common in corporate applications where multiple team members must use the software. As the team grows, the cost rises with each additional user. This pricing plan is scalable, and charges are based on the number of users who benefit from the product.
3) Usage-Based Pricing
Usage-based pricing charges clients based on their actual program usage. This approach is commonly used in SaaS services that require data storage or API calls. For example, a cloud storage provider can charge clients based on the volume of data saved or transported. This price is flexible and cost-effective for enterprises with changing usage patterns.
4) Freemium Model
The freemium model gives a free base version of the software with the opportunity to upgrade to a premium plan for more features and support. This concept attracts many users and helps them test the software before committing to a paying plan. Dropbox and Slack are examples of SaaS startups that use the freemium pricing model.
5) Flat-Rate Pricing
Flat-rate pricing allows consumers to access all software capabilities for a single, fixed charge. This concept simplifies pricing and appeals to clients who value certainty in their spending. However, it can not be as adaptable or scalable as other models, which makes it less popular for large-scale or corporate projects.
6) Custom Pricing
Enterprise-level SaaS solutions give customized pricing based on the business’s specific demands. This could include customized features and increased security or compliance. Custom pricing is negotiated directly with the SaaS provider which makes it ideal for large enterprises with specific needs.
Challenges and Risks of SaaS
While SaaS has numerous advantages, it also has some issues and risks. Security concerns are important since sensitive data is stored elsewhere and can be subject to breaches. Dependence on internet connectivity can cause problems if there are network faults.
Furthermore, firms can encounter data integration and interoperability issues with existing systems. Another risk is vendor dependability, which requires businesses to trust their SaaS provider to maintain service quality and uptime.
Controlling subscription costs and interpreting licensing conditions can be difficult and result in unseen expenses. These difficulties must be carefully considered and managed.
Conclusion
Software as a Service is an adaptable and easy way to get software through the Internet. It has many benefits, like cost savings and automated updates. Many companies use SaaS for communication and customer relationship management purposes. SaaS helps you focus on getting work done efficiently by ending the need for complex installations and maintenance.
FAQs
Q-1) What Is a SaaS Product?
A SaaS product is a software application hosted and supplied online by a third-party source.
Q-2) What Are the Examples of SaaS?
Some well-known examples of SaaS models are Dropbox, Google Workspace, and Salesforce.
Q-3) What’s the Difference Between Cloud and SaaS?
Cloud computing provides a comprehensive foundation for delivering computing services. SaaS is a subset of cloud computing that focuses on software delivery.