Code refactoring has always been caught between two competing priorities: the need for continuous improvement and the reality that developers spend limited time on it. Research shows that StarCoder2 reduces code smells by 20.1% more than human developers when performing automated refactorings. But here’s the problem: most teams still treat refactoring as a manual, intermittent task rather than a continuous, automated process.
At Dextra Labs, we help enterprises and SMEs across the UAE, USA, and Singapore implement LLM-powered development workflows that make refactoring continuous rather than occasional. The difference between code that gradually degrades and code that improves over time isn’t developer discipline—it’s having the right automation in place.
This guide explores how to use LLMs for continuous code refactoring in production environments, drawing from cutting-edge research and real-world implementation patterns.
The Refactoring Challenge: Why Manual Approaches Don’t Scale
Traditional refactoring faces three fundamental problems:
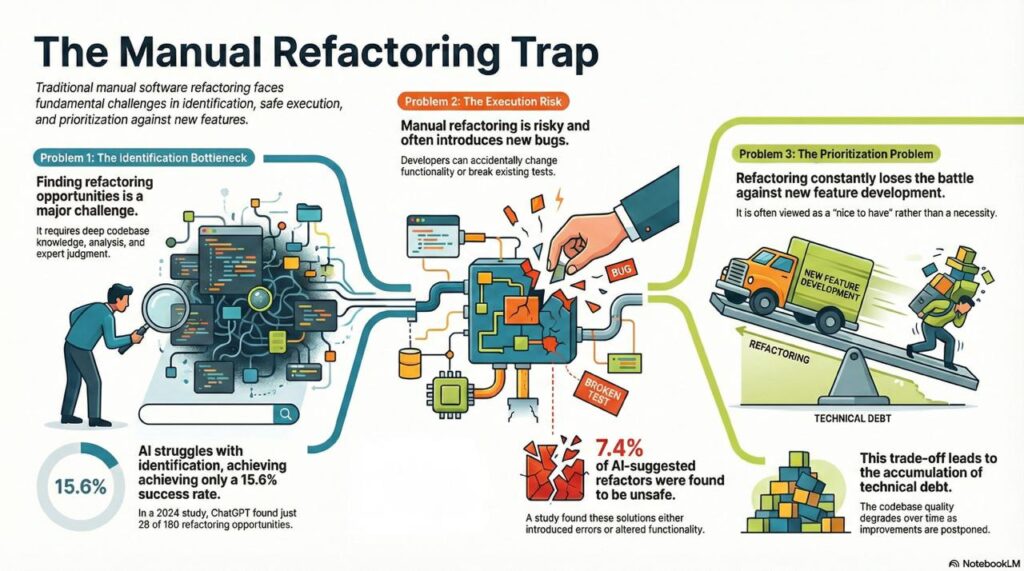
1. Identification Bottleneck
Developers must manually identify where refactoring is needed. Even with IDE support, this requires:
- Deep understanding of the codebase
- Time to analyze code quality metrics
- Judgment about which improvements matter most
Research from 2024 shows that when given raw Java documents without guidance, ChatGPT identified only 28 out of 180 refactoring opportunities (15.6% success rate) (arXiv). The problem isn’t just tool capability—it’s that identifying refactoring opportunities requires context that’s hard to communicate.
2. Execution Risk
Manual refactoring introduces bugs. Even experienced developers occasionally:
- Change functionality while refactoring
- Break existing tests
- Introduce syntax errors
- Create regressions in edge cases
A 2024 empirical study found that 13 out of 176 refactoring solutions suggested by ChatGPT (7.4%) were unsafe, either changing functionality or introducing errors (arXiv). The risk is real—which is why many teams avoid refactoring except when absolutely necessary.
3. Time and Priority Trade-offs
Refactoring competes with feature development. Product managers push for new capabilities, and technical debt accumulates because refactoring feels like “nice to have” rather than “must have.”
The solution isn’t more developer discipline, it’s automation that makes refactoring continuous, safe, and nearly invisible.
Also read: Enterprise-Grade LLM Deployment: A Roadmap for CTOs in Tech-Driven Startups
How LLMs Change the Refactoring Game?
Large language models bring three capabilities that traditional tools lack:
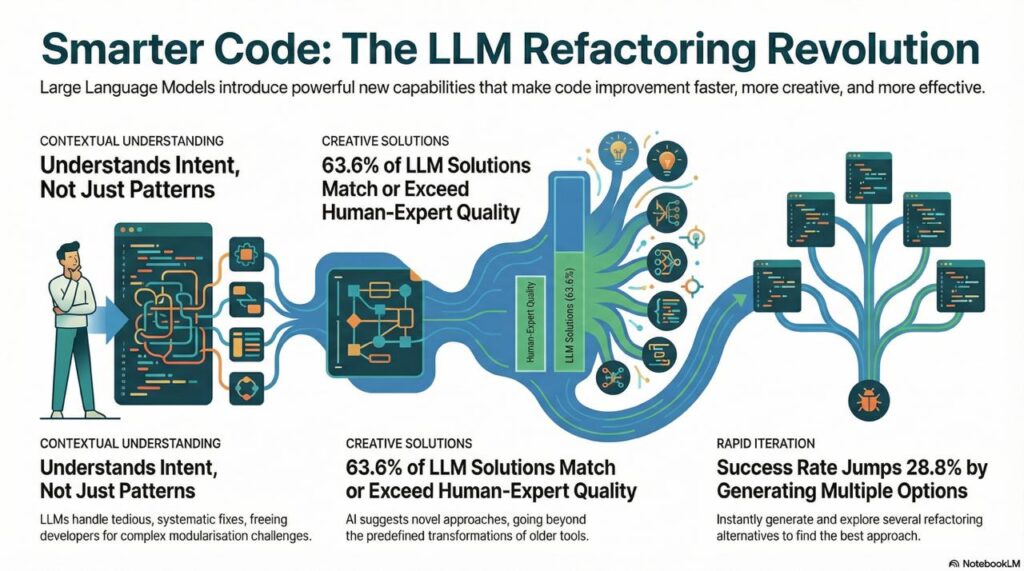
1. Contextual Understanding
LLMs don’t just match patterns—they understand what code does. Research shows that LLMs excel at systematic refactorings like reducing Long Statements, Magic Numbers, and Long Identifiers, while developers handle complex issues like Broken Modularization better (arXiv).
This division of labor is key: LLMs can handle the tedious, repetitive improvements that developers know they should make but never prioritize.
2. Creative Solutions
Unlike rule-based tools that apply predefined transformations, LLMs can suggest novel approaches. When comparing LLM-generated refactorings to human-written ones, 63.6% of ChatGPT’s solutions were comparable to or better than those constructed by human experts (arXiv).
3. Rapid Iteration
LLMs can generate multiple refactoring options instantly. Research found that generating five refactorings per input increased the unit test pass rate by 28.8% (arXiv). This means you can quickly explore alternatives and choose the best approach.
Also Read: LLM Use Cases Explained – Useful Examples Across Industries 2026
The Production Architecture: Making LLM Refactoring Safe
Stage 1: Opportunity Detection
Automated Code Analysis: Run static analysis tools to identify code smells and quality issues across your codebase.
Priority Scoring: Rank potential refactorings by:
- Impact on maintainability metrics
- Frequency of code changes in affected areas
- Complexity of required changes
Context Assembly: For each candidate, gather:
- The problematic code
- Surrounding context (calling functions, dependencies)
- Test coverage information
- Recent commit history
Stage 2: LLM-Guided Generation
Prompt Engineering: The quality of refactoring suggestions depends heavily on how you structure prompts. Research shows that explaining expected refactoring subcategories increased ChatGPT’s success rate from 15.6% to 86.7%(arXiv).
Effective prompts include:
- The specific type of refactoring needed (Extract Method, Rename Variable, etc.)
- The reason for refactoring (code duplication, long statement, magic number)
- Constraints (must maintain test coverage, preserve API compatibility)
One-Shot Prompting: Including an example refactoring in your prompt improves results. Research shows one-shot prompting yields 34.51% unit test pass rate, a 6.15% improvement over zero-shot (arXiv).
Stage 3: Safety Validation (RefactoringMirror Pattern)
This is the critical safety layer that makes LLM refactoring production-ready. The RefactoringMirror approach works as follows:
- LLM generates refactored code
- Detect what refactorings were applied by comparing original and refactored versions
- Reapply detected refactorings using tested refactoring engines (like IntelliJ IDEA or JDeodorant)
- Compare outputs: If the engine-generated version matches the LLM version, it’s safe
Research shows RefactoringMirror accurately identified and reapplied 94.3% of LLM refactorings and successfully avoided all buggy solutions (arXiv).
Stage 4: Test Execution and Verification
Before accepting any refactoring:
Run Full Test Suite: All existing tests must pass
Check Code Coverage: Coverage shouldn’t decrease
Static Analysis: Verify that quality metrics improved
Behavioral Equivalence: Use tools like equivalence checkers to confirm functional preservation
Stage 5: Human Review and Integration
Automated Pull Requests: Create PRs for approved refactorings with:
- Clear explanation of what changed and why
- Quality metrics before and after
- Links to relevant issues or technical debt tickets
Staged Rollout: Don’t refactor everything at once. Start with:
- Low-risk, high-value modules
- Code with good test coverage
- Areas actively being developed (easier to verify correctness)
Also Read: Best LLM for Coding: Choose the Best Right Now (2026 Edition)
Prompt Engineering for Better Refactorings
Research consistently shows that how you prompt matters as much as which model you use. Here are proven techniques:
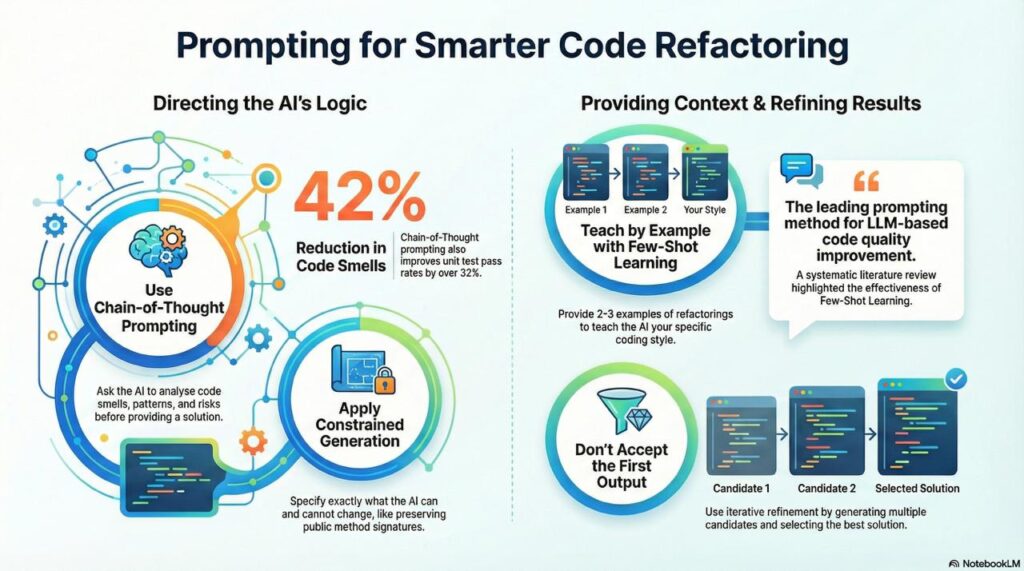
Chain-of-Thought Prompting
Ask the LLM to explain its reasoning;
Before refactoring, analyze:
1. What code smells are present?
2. Which refactoring patterns would address them?
3. What risks does each approach introduce?
Then provide your refactored solution.
Research shows chain-of-thought prompting achieves 32.22% unit test pass rate and 42.34% smell reduction, improving on zero-shot by 3.86% and 2.89% respectively (arXiv).
Constrained Generation
Specify exactly what the LLM can and cannot change:
- “Preserve all public method signatures”
- “Do not modify the class interface”
- “Keep all existing comments”
- “Maintain alphabetical ordering of imports”
Few-Shot Learning
Provide 2-3 examples of refactorings in your codebase’s style. This teaches the LLM your conventions and patterns. A systematic literature review found that few-shot learning is the leading prompting method for LLM-based code quality improvement (ScienceDirect).
Iterative Refinement
Don’t accept the first output. Generate multiple candidates and either:
- Select the best manually
- Use automated scoring (test pass rate, static analysis metrics)
- Combine elements from multiple solutions
Also Read: 10 Engineering Lessons for Building Successful LLM Applications
What LLMs Excel At (and What They Struggle With)?
Understanding LLM strengths and weaknesses helps you deploy them effectively:
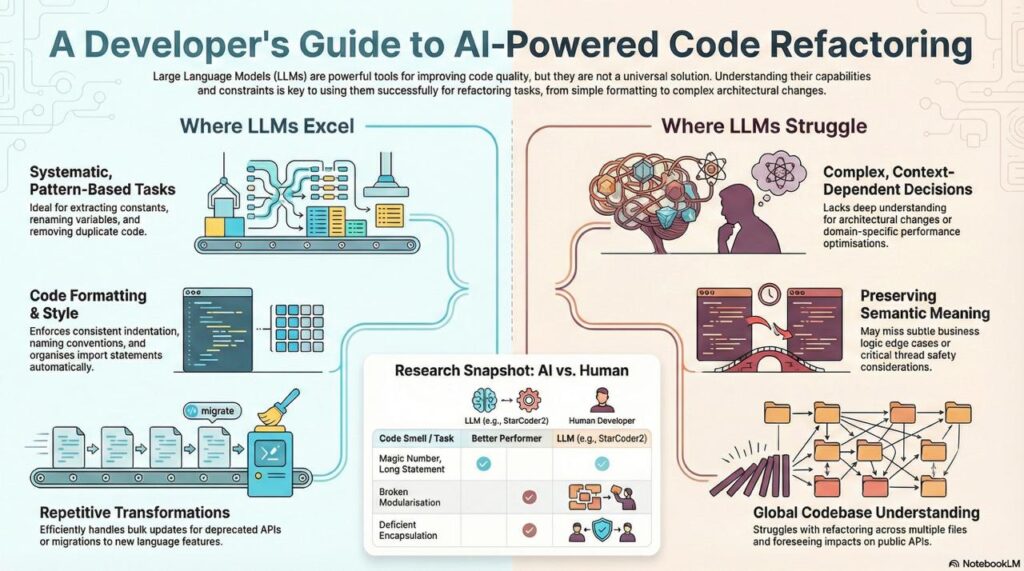
LLMs Excel At:
Systematic, Pattern-Based Refactorings:
- Extracting magic numbers to constants
- Renaming variables for clarity
- Breaking long methods into smaller ones
- Removing code duplication
Research confirms StarCoder2 excels in reducing Long Statement, Magic Number, Empty Catch Clause, and Long Identifier code smells (arXiv).
Formatting and Style:
- Consistent indentation
- Naming convention enforcement
- Comment formatting
- Import organization
Repetitive Transformations:
- Converting loops to streams
- Updating deprecated API usage
- Migrating to newer language features
LLMs Struggle With:
Context-Dependent Decisions:
- Architectural refactorings (splitting classes, reorganizing modules)
- Performance optimizations requiring profiling data
- Domain-specific patterns
Research shows developers perform better at fixing Broken Modularization, Deficient Encapsulation, and Multifaceted Abstraction (arXiv).
Semantic Preservation:
- Edge cases in business logic
- Subtle behavioral differences
- Thread safety considerations
- Resource management changes
Global Understanding:
- Refactorings spanning multiple files
- Impact on downstream consumers
- Breaking changes in public APIs
Also Read: Framework Migration Made Easy with AI: How to Move from Java to Node.js (or Any Stack)
Tools and Integration
LLMs for Code Refactoring
StarCoder2: Open-source, optimized for code. Research shows it achieves 46.3% on HumanEval pass@1 (arXiv). Good for self-hosted deployments.
GPT-4: Strong general reasoning, good at explaining refactorings. Best for complex, creative transformations.
Claude: Excellent at following constraints and maintaining context. Works well for large-scale refactorings.
Gemini: Fast and cost-effective. Suitable for batch processing many small refactorings.
Static Analysis Tools
SonarQube: Comprehensive code quality analysis
PMD: Java-specific smell detection
Checkstyle: Style and convention enforcement
SpotBugs: Bug pattern detection
Refactoring Engines
IntelliJ IDEA: Robust refactoring for Java
JDeodorant: Research-backed refactoring tool
Eclipse JDT: IDE-integrated refactorings
CI/CD Integration
GitHub Actions: Automate refactoring in PR workflows
GitLab CI: Run nightly refactoring jobs
Jenkins: Custom refactoring pipelines
Also Read: Boost Developer Productivity by 40%: Real Use Cases of AI in Software Development
Challenges and Limitations
Despite promising results, LLM-driven refactoring faces real challenges:
1. Reliability Concerns
A systematic literature review found that refactored code by LLMs is not reliable (ScienceDirect). This is why safety validation (like RefactoringMirror) is non-negotiable.
2. Context Window Limitations
LLMs have finite context windows. Refactoring large files or understanding cross-file dependencies remains challenging.
Solutions:
- Break large files into logical units
- Provide focused context (only relevant methods)
- Use retrieval to pull in distant dependencies
3. Cost at Scale
Running LLMs on every code change gets expensive. Optimize by:
- Targeting high-value refactorings first
- Using smaller models for simple transformations
- Caching common patterns
- Batching similar refactorings
4. Integration Friction
Developers resist tools that feel like extra work. Success requires:
- Seamless IDE integration
- One-click acceptance of suggestions
- Clear explanations of why refactoring helps
- Opt-out options for false positives
What are the Best Practices from Production Deployments?
Start Small and Focused
Don’t try to refactor your entire codebase. Begin with:
- A single module or package
- One type of refactoring (e.g., Extract Method)
- Code with good test coverage
Measure Everything
Track:
- Acceptance rate of suggestions
- Bug introduction rate
- Time saved
- Quality metric improvements
Build Developer Trust
LLM refactoring succeeds when developers trust it. Build trust by:
- Showing clear before/after comparisons
- Explaining the reasoning
- Making it easy to reject bad suggestions
- Celebrating successful improvements
Iterate on Prompts
Your first prompts won’t be perfect. Continuously improve based on:
- Which suggestions get accepted vs. rejected
- What types of errors occur
- Developer feedback
The Future: Self-Improving Codebases
The trajectory is clear: codebases won’t just be maintained—they’ll actively improve themselves. Research is moving toward:
Autonomous Refactoring Agents: LLMs that proactively identify and fix issues without human prompting
Learning from Feedback: Systems that improve prompts based on which refactorings developers accept
Cross-Project Learning: Models trained on millions of refactorings across open-source projects
Semantic Understanding: Better comprehension of business logic and domain constraints
A position paper at ICSE 2025 examines the limitations of existing LLM-based refactoring and proposes research directions for improving quality and reliability (ICSE). The field is advancing rapidly.
Conclusion: From Periodic to Continuous
The difference between LLM-assisted refactoring and traditional approaches isn’t just speed—it’s continuity. Manual refactoring happens in bursts, when technical debt becomes unbearable. LLM-powered refactoring happens constantly, as part of normal development flow.
Research shows the technology is ready: 20.1% better smell reduction, 63.6% of solutions comparable to human experts, and 94.3% safe reapplication rate with proper validation (arXiv).
What’s missing isn’t capability—it’s implementation. At Dextra Labs, we help enterprises and SMEs across the UAE, USA, and Singapore build the infrastructure for continuous, safe, LLM-powered refactoring.
The codebases that win aren’t those that start cleanest—they’re those that improve continuously. And in 2025, continuous improvement means LLM automation.