The rapid advancement of technology has propelled the Fintech sector into the spotlight, reshaping conventional banking and financial services. At the heart of this revolution lies the extensive use of data, powering innovations such as algorithmic trading, tailored financial guidance, and sophisticated risk evaluation models. Yet, amid this data-driven evolution, ethical dilemmas loom large, especially regarding the responsible handling and application of confidential financial data. In this blog post, we will navigate the intricacies surrounding ethical considerations within Fintech data management, examining their implications for businesses and consumers alike.
Data Privacy and Security
One of the primary ethical concerns in Fintech revolves around data privacy and security. Fintech companies collect extensive personal and financial data from users, ranging from transaction histories to behavioral patterns. Safeguarding this data from breaches and unauthorized access is not only a legal requirement but also an ethical imperative. Failure to adequately protect sensitive financial information can lead to severe consequences, including identity theft, financial fraud, and reputational damage to the Fintech firm.
To address the critical concerns surrounding data privacy and security in Fintech, companies must adopt comprehensive measures to protect sensitive information. Robust data encryption protocols and access controls are essential components of a strong defense against cyber threats, ensuring that data remains secure both in transit and at rest.
Additionally, adherence to regulatory frameworks such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is non-negotiable, as it not only establishes legal requirements but also reinforces a commitment to respecting user privacy rights. By prioritizing data privacy and security, Fintech firms demonstrate their dedication to safeguarding customer data, thereby fostering trust and confidence among consumers while mitigating the significant risks associated with potential data breaches.
Transparency and Accountability
Fintech companies need to maintain transparency regarding how they collect data, their usage policies, and how they share this information. By providing clear and easily understandable privacy policies, written in simple language, they empower consumers to make informed choices about sharing their personal data. Additionally, Fintech firms must institute mechanisms for accountability, such as conducting regular audits, implementing internal controls, and subjecting themselves to oversight by regulatory bodies.
Furthermore, transparency in Fintech extends beyond data privacy policies to encompass the algorithms and AI models underpinning financial decision-making processes. With algorithmic decision-making gaining prominence in critical areas such as credit scoring and loan approvals, ensuring the fairness and explainability of these algorithms becomes paramount. It’s imperative to employ robust bias detection and mitigation techniques to prevent discriminatory outcomes and uphold principles of fairness and equality. Moreover, providing users with insights into how their data influences automated decisions fosters greater transparency and accountability, empowering individuals to understand and challenge the outcomes of algorithmic processes. By prioritizing transparency in algorithmic decision-making, Fintech companies not only enhance trust and credibility but also promote fairness and inclusivity in financial services.
Ethical Use of Data
This crucial process entails using financial information responsibly and ethically, with due consideration for the welfare of individuals and society at large. Fintech companies must refrain from exploiting user data for unethical purposes, such as targeted advertising or predatory lending practices. Instead, they should leverage data to enhance financial inclusion, improve risk assessment models, and empower consumers to make better financial decisions.
In addition to ethical data management practices, Fintech firms must prioritize the ethical sourcing of data, ensuring that the methods used for data acquisition are not only legal but also ethically sound. This involves obtaining explicit consent from users before collecting their data, thereby respecting individuals’ autonomy and privacy rights. Moreover, adherence to principles of data minimization and anonymization is crucial, ensuring that only necessary data is collected and that personally identifiable information is adequately protected. By upholding these ethical standards in data sourcing, Fintech companies not only mitigate the risk of regulatory penalties and reputational damage but also build sustainable business models grounded in trust and integrity, ultimately prioritizing the interests of both consumers and society as a whole.
Key Impacts
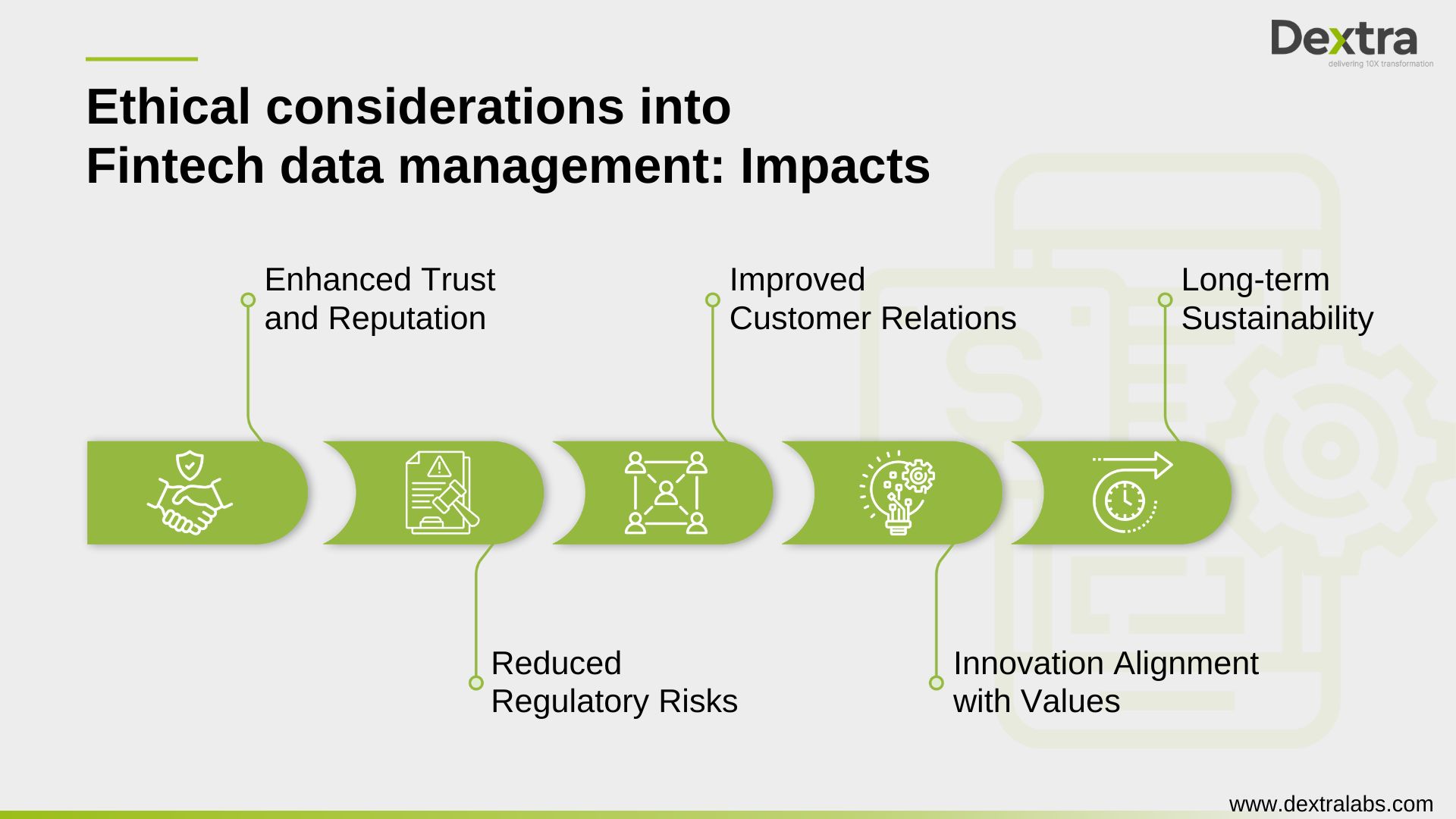
Here are key impacts of integrating ethical considerations into Fintech data management:
Enhanced Trust and Reputation |
|
Reduced Regulatory Risks |
|
Improved Customer Relations |
|
Innovation Alignment with Values |
|
Long-term Sustainability |
|
Conclusion
Ethical considerations in Fintech data management are paramount in ensuring the responsible and sustainable use of financial information. By prioritizing data privacy, transparency, and ethical use, Fintech companies can build trust with consumers, mitigate risks, and drive positive social impact. As the Fintech industry continues to evolve, ethical data management must remain at the forefront of innovation, guiding the development of solutions that benefit both businesses and society as a whole.