Enterprise decision-making is changing quickly. Most organizations have outgrown the limits of batch analytics and periodic reporting cycles. Teams now operate in environments where customer behavior shifts minute-to-minute, compliance checks must run continuously, and operations depend on accurate updates in near real time.
Static dashboards and once-a-day refreshes aren’t enough. What companies need is the ability to act the moment information arrives — not hours later.
This growing demand is driving interest in Context Engines: architectures that combine real-time data pipelines, AI agents, and workflow orchestration to support or automate decisions at scale. At Dextralabs, we work with enterprises to design and implement these systems so they can make decisions faster, more accurately, and with full visibility.
What Is Decision Automation — And Why Real-Time Data Matters?
Decision automation is the practice of letting systems, instead of humans, decide outcomes for high-frequency or rule-driven tasks. In its earlier form, this meant pairing business rules with occasional model predictions inside operational systems.
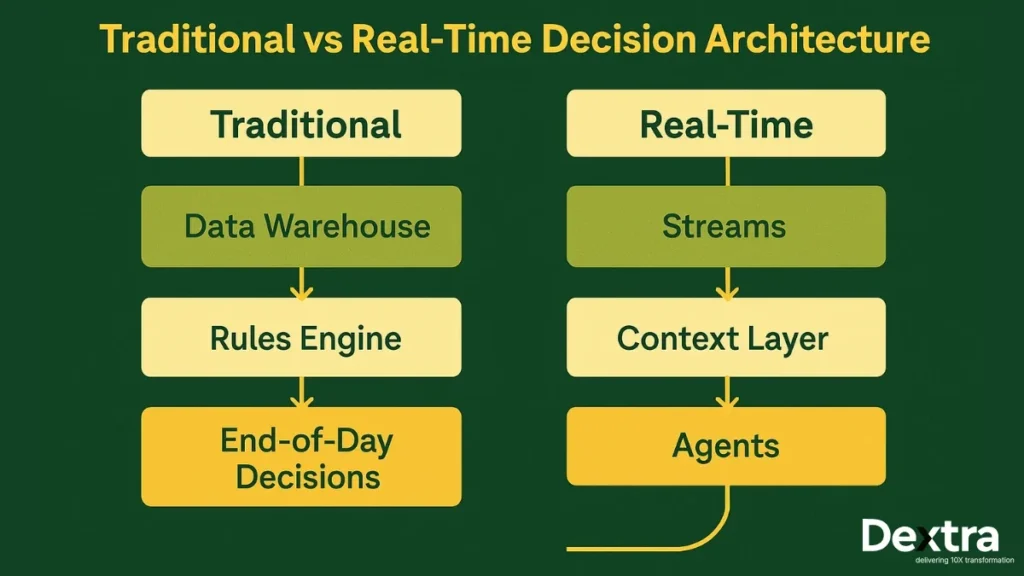
But this older model has limits:
- Data was often outdated by the time rules ran
- Models were refreshed slowly
- Decisions were constrained by batch updates
Modern decision automation looks very different. With continuous data streams and event-driven triggers, decisions can be made based on the most current information. AI agents can review context, evaluate rules or models, and carry out actions immediately.
A complete decision automation stack typically includes:
- Business rules for guardrails and compliance
- ML/AI models for scoring, ranking, pattern recognition
- Real-time data pipelines that deliver reliable, fresh inputs
- Agents that interpret the situation and select actions
When all these pieces work together, organizations can reduce manual workloads, shorten operational cycles, improve consistency, and handle far more decisions than any human team could reliably process.
The Pillars of a Context Engine Architecture
A Context Engine brings together several layers that collectively enable reliable, automated decisions. Breaking them down helps leaders understand how each layer contributes to overall performance.
Real-Time Data Pipelines
This is the foundation. Pipelines continually collect data from databases, SaaS systems, APIs, event logs, IoT devices, and other streams. Data is transformed, validated, and made available so agents always act on the latest state — not outdated snapshots.
Context Modeling & State Layer
Raw events rarely provide enough meaning on their own. The context layer builds structured views of what’s happening:
- customer history
- business state
- environmental factors
- recent sequences of events
Agents can query this state to understand both what is happening and what has happened.
Autonomous Agents / Decision Agents
These agents examine context, evaluate rules and model outputs, and choose actions. Depending on the use case, they may:
- suggest decisions
- take direct actions
- escalate items to humans
- run multi-step workflows or checks
Agents can be simple and deterministic, or more advanced and reasoning-driven.
Decision Orchestration & Workflow Engine
Even the most advanced agent requires guardrails. The orchestration layer coordinates:
- triggers
- agent calls
- rule checks
- fallbacks
- human-in-loop reviews
This ensures decisions remain consistent, controlled, and auditable.
Monitoring, Governance & Audit Layer
Every decision must be traceable. This layer captures:
- data lineage
- decision logs
- agent actions
- approval steps
- compliance checks
For regulated industries, this is essential.
Feedback & Continuous Learning Loop
A robust system must improve over time. Feedback loops capture results, track model drift, and update rules or logic based on actual outcomes.
These pillars together create a reliable, enterprise-grade architecture for automated decision-making.
Why Enterprises Are Adopting Agent-Driven Decision Automation?
Agent-driven decision automation is becoming standard because it directly improves operational performance. Here are common areas where companies are seeing impact:
Finance and Risk
- Continuous credit scoring based on transaction streams
- Real-time fraud detection
- Automated risk flags for unusual activity
Operations and Supply Chain
- Automatic reorders triggered by live inventory signals
- Demand forecasts that update as new data arrives
- Intelligent routing for logistics and fulfillment
Customer Experience and Support
- Routing tickets or issues to the right team as soon as they’re submitted
- Personalized product or service recommendations
- Automated responses using domain-specific agents
SaaS and Internal Platforms
- SLA tracking and alerting
- Automated compliance checks
- Continuous anomaly detection in application events
Across all these domains, the value is clear: shorter decision cycles, fewer manual interventions, fewer errors, better scalability, and improved oversight.
Key Challenges & How to Manage Them:
While Context Engines offer major benefits, they introduce engineering, operational, and governance challenges that leaders should be aware of.
Challenge: Data quality and consistency
Real-time data can be messy. Without strong validation, even one malformed event can cause incorrect decisions.
Mitigation: schema enforcement, data contracts, automated validation.
Challenge: Latency or throughput issues
High-frequency workflows can slow if pipelines or models aren’t optimized.
Mitigation: streaming-first design, efficient message formats, proper indexing, and backpressure handling.
Challenge: Unintended agent behavior
Agents acting without proper constraints can make decisions that impact compliance or customer experience.
Mitigation: decision gating, rule-first boundaries, human approvals for sensitive actions.
Challenge: Governance and visibility
Without careful planning, decisions become difficult to trace or audit.
Mitigation: full decision logs, lineage tracking, versioning for rules and models.
Challenge: Scaling complexity
As new agents and workflows are added, the system can become hard to maintain.
Mitigation: modular architecture, clear interfaces, strong documentation, and standardized workflows.
Addressing these areas early ensures reliability and reduces long-term operational overhead.
How Dextralabs Builds Context Engines & Agentic Decision Systems?
Dextralabs helps enterprises design and deploy Context Engines built for real-world scale. Our approach is structured to minimize risk and align closely with business goals.
Assessment & Strategy
We evaluate existing systems, decision workflows, and operational constraints. This clarifies where automation brings the highest value and how to integrate it with existing infrastructure.
Design & Architecture
We design end-to-end architectures that include:
- real-time pipelines
- context layers
- agent frameworks
- orchestration
- governance models
The design reflects both technical requirements and compliance needs.
Implementation & Integration
Our team builds and deploys pipelines, sets up decision agents, and integrates them with internal systems such as ERP, CRM, and operational databases.
Monitoring & Governance
We implement observability, auditing, safety checks, and alerts to ensure decisions remain reliable and transparent.
Continuous Optimization
Once deployed, we refine rules, improve agents, add context features, and scale the system to additional workflows.
Dextralabs brings experience across financial services, logistics, SaaS, and enterprise operations — helping organizations build systems that are dependable and ready for production.
A Practical Implementation Blueprint:
For executives and technical leads planning to build such a system, here’s a high-level roadmap:
Phase 0: Discovery & Requirements
Identify decision points, business goals, data sources, and KPIs.
Phase 1: Data Pipeline Setup
Implement real-time ingestion, ETL/ELT workflows, validation rules, and standardization.
Phase 2: Context Layer Design
Define user context, business state, historical patterns, and temporal context.
Phase 3: Agent & Orchestration Build
Design agent roles, define decision logic, add guardrails, and incorporate human approvals.
Phase 4: Governance & Observability
Add monitoring for data quality, model outputs, decision logs, and audit trails.
Phase 5: Pilot & Validation
Test decisions in controlled environments, measure accuracy, and gather internal feedback.
Phase 6: Scale & Optimize
Roll out fully, introduce new workflows, track performance, and update decision logic as conditions change.
This blueprint helps organizations progress from planning to production with fewer risks.
Final Words:
Enterprises that rely on delayed or incomplete information will struggle to make dependable decisions at the speed their operations now demand. Context Engines — combining real-time data, AI agents, and well-governed workflows — are becoming essential for teams that need accuracy, consistency, and transparency.
Building these systems requires careful architectural planning, strong data practices, and reliable governance. This is where Dextralabs can help.
If your organization is exploring decision automation or evaluating how to introduce AI agents into your workflows, consider partnering with Dextralabs for a Context Engine Readiness Assessment or a targeted proof-of-concept.
FAQs:
What is a context engine in AI decision automation?
A context engine is a system that combines live data, stateful context, agents, and orchestration to support or automate decisions. It helps AI systems interpret events with full understanding of user, business, and environmental activity.
How does real-time AI differ from batch AI?
Real-time AI processes events as they occur. Batch AI processes data at scheduled intervals. Real-time systems enable immediate decisions; batch systems give trend-level insights but cannot act instantly.
Can autonomous agents replace human decision-making entirely?
Not in most enterprise scenarios. Agents typically automate repeatable or high-volume tasks, while humans remain responsible for oversight, policy decisions, and exceptions.
What tools are often used for real-time data pipelines?
Common options include Kafka, Flink, Spark Structured Streaming, Materialize, and cloud-native streaming services. The best choice depends on throughput, latency, and existing infrastructure.
How do you maintain auditability in automated decision systems?
By logging every decision, capturing context inputs, tracking model versions, and storing rule configurations. This allows teams to explain why any decision was made.